Appearance
Webhook
Configuration
Write Honeypot events directly to an HTTP(s) endpoint by following these steps:
From the connectors page, select , and then click .
An example configuration will appear in the tab. Update the connection information with the appropriate values for your webhook.
Geoblock Warning
If you have configured any geo-fencing rules, you should always set
useQueueto true. This is because certain proxies and firewall rules will block webhooks that are invoked directly from your honeypot if the request stems from a blocked region.json{ // Webhook endpoint URL "url": "", // Basic auth username (optional) "basic_auth_user": "", // Basic auth password (optional) "basic_auth_pass": "", // key-value headers (optional) "headers": {}, // Use queue to buffer events (default: false) "useQueue": false, // Optional URL to send events to if the webhook fails. // Currently only works if useQueue is false. "errorUrl": "" }From the tab, use the filter builder to control which events should be written to the connector.
Click to test the connector. If the webhook is configured properly, you will see either a status of
200or a message that saysQUEUED(ifuseQueueistrue).Click to save the connector.
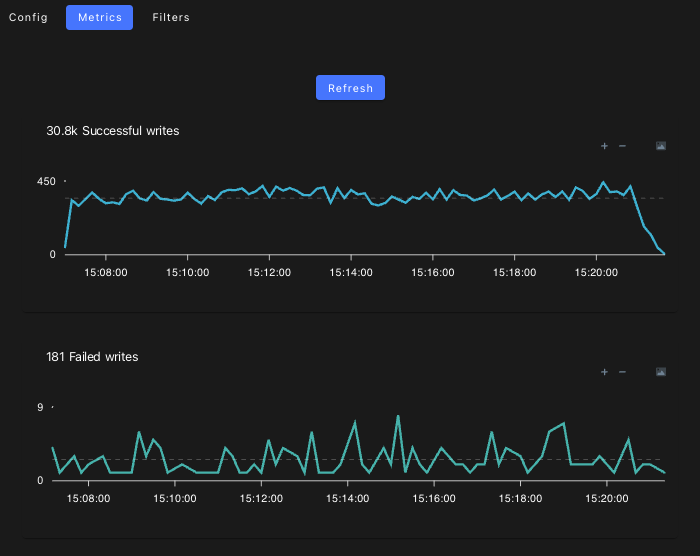
From the tab, you can monitor the traffic to your webhook connector.
Payload
Each time the webhook is invoked, an event payload will be included in the POST request.
For more information about the structure of the payload, see:
Error Handling
You can configure the errorUrl property in the webhooks config to provide an alternative URL to send the request to if the primary URL fails. Whenever Honeypot falls back to the errorUrl, it will add the following property to the event payload:
json
{
"is_error": true
// rest of the the event payload
}